The dwarf tapeworm is a tapeworm (cestode) that is found everywhere and whose only host is humans.

Content
Structure
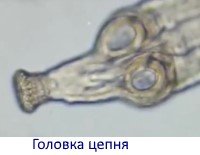
The ribbon-like body consists of a head, neck and strobila. The length of the parasite is 5-50 mm. The head is equipped with 4 suckers and a proboscis with a corolla of 20-30 hooks. With the help of a proboscis and suckers, the worm is fixed on the mucous membrane of the human small intestine. Thanks to the suckers, the tapeworm can move through the intestines, changing its place of attachment.
The body (strobilus) consists of 200-300 segments. The middle segments are hermaphroditic, and the posterior mature segments contain a uterus with eggs.
The eggs are oval, 40x53 microns in size.
Life cycle
The development cycle begins and ends in the human body, which serves as both an intermediate and definitive host for the parasite.
A person becomes infected by ingesting mature tapeworm eggs. In the small intestine, oncospheres emerge from the eggs and actively penetrate the villi. Passing through several stages of development, they turn into cysticercoids, which contain the head and neck of the worm. Cysticercoids destroy the intestinal villi and enter the intestinal lumen, attaching between the villi. After 14-15 days they develop into sexually mature individuals.
The posterior mature segments are separated from the strobila and destroyed in the intestine, the eggs released from them with feces are released into the external environment.
The lifespan of a dwarf tapeworm is about 2 months.
Sometimes, when the human body is weakened, re-infection occurs when the eggs do not leave the intestines, but again penetrate into the villi and repeat the development cycle, significantly increasing the infection.
In rare cases, insects (meal beetle, some types of fleas) become infected with larvae; mice and rats become the final host.
Hymenolepiasis
 Infection with dwarf tapeworm causes the disease hymenolepiasis and is accompanied by symptoms of predominantly damage to the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Infection with dwarf tapeworm causes the disease hymenolepiasis and is accompanied by symptoms of predominantly damage to the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Every year in Russia, 5-7 thousand cases of infection with this helminth are registered, the incidence is 3-4 per 100 thousand population. Children get sick 3-3.5 times more often.
The incubation period is about 2 weeks.
Routes of infection
This type of disease is contagious, that is, with the possibility of infection through contact. This is due to the fact that the eggs enter the external environment mature and can cause infection if they enter the gastrointestinal tract.
The stability of eggs in the external environment is short - several hours. In kindergartens and nurseries, if sanitary and hygienic standards are not observed, more than half of the children can become infected.
The source of infection is humans. You can become infected through household items, toys, and food products contaminated with helminth eggs. Insects play an important role in food contamination.
Health effects
The main pathological factor is damage to the mucous membrane of the small intestine by larvae and adult helminths. Developing in the villi of the small intestine, the larvae cause their enlargement, swelling, degeneration and necrosis with the formation of ulcers that can reach the muscle layer.
With massive infection, when a large number of helminths simultaneously live in the intestines and they move along the mucous membrane and change places of attachment, extensive defects in the intestinal mucosa are formed. However, due to the high compensatory capacity of the small intestine, the condition of patients can remain satisfactory for quite a long time.
If the infection is not treated, then over time the enzymatic and motor functions of other digestive organs - the stomach, liver, biliary tract - are disrupted and dysbiosis .
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms depends on the state of a person’s immunity. Some people do not become infected even in experiments where they specifically consume dwarf tapeworm eggs. Almost a third of those infected are asymptomatic.
The following symptoms may occur with hymenolepiasis:
- decreased or lack of appetite,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- dull aching pain in the abdomen not associated with eating,
- unstable chair,
- diarrhea,
- salivation,
- general fatigue
- decreased motor activity,
- memory impairment,
- headache,
- increased nervous excitability,
- fainting,
- somnambulism,
- allergies (skin itching, angioedema, rhinitis, asthmatic bronchitis, asthma attacks),
- muscle cramps, epileptic-type seizures,
- anemia,
- fever.
Long-term infection leads to a decrease in the acid-forming function of the stomach, enzymatic disorders in the intestines, enlarged liver, enlarged lymph nodes in the abdominal cavity, decreased blood pressure, signs of myocardial dystrophy, decreased and deformed R waves in all leads on the ECG.
Severe complications may include dysbacteriosis, mesenteric lymphadenitis, exacerbation of gastric and duodenal ulcers .
Diagnostics
Infection with dwarf tapeworm is detected by examining stool for worm eggs. The periods of excretion of eggs by worms alternate with pauses, so it is necessary to take a stool test three times with an interval of 15-20 days.
If eggs cannot be detected, and symptoms of infection are present, then it is recommended to give the patient niclosamide in a reduced dose (0.5-1.0 g) along with 1 g of a laxative the evening before the test. Niclosamide destroys the tapeworm strobila and a large number of eggs are released into the feces.
Treatment
 This disease requires systematic treatment. This is due to the possibility of repeated intraintestinal self-infections and the pathological effect of worms on health.
This disease requires systematic treatment. This is due to the possibility of repeated intraintestinal self-infections and the pathological effect of worms on health.
In addition to antiparasitic drugs, it is necessary to carry out symptomatic treatment simultaneously with a set of preventive measures.
On the eve of taking the antihelminthic drug, you should follow a slag-free diet, which includes broths, purees, jelly, kefir, and ground meat.
For therapy, praziquantel , which is used once an hour after meals with a small amount of water.
In case of massive infection, repeated use is recommended after 7-10 days. The effectiveness of treatment is 90%.
Another drug used is niclosamide . This remedy requires a course of treatment and is less effective (70%).
After completing the course, observation by a doctor is recommended for 6 months. Control stool tests are taken 3 times during this period - after 3 weeks, 1 and 6 months.
If there is no effect from treatment, the course of taking the drug is repeated up to 3 or more times. In this case, the period of clinical observation is increased to 1 year, 6 control stool examinations are carried out. The patient is removed from clinical observation after 6 negative tests.
Forecast
After infection, about half of children and 85% of adults recover spontaneously within a year. But if re-infection occurs or the body cannot cope with the disease, then it becomes chronic and relapsing and can last for years, causing harm to health.
Prevention
Preventive stool testing is indicated once a year for the following categories of people:
- children and staff of preschool children's institutions, primary school students,
- visitors to swimming pools,
- patients in children's hospitals.
If there is an infected person in the house, it is necessary to disinfect household items and monitor personal hygiene.







