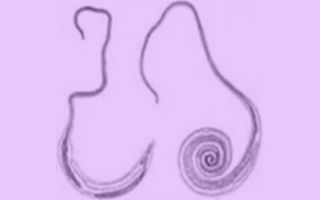
Whipworm or whipworm is a nematode helminth that parasitizes the human colon .
Content
Structure
The body of the whipworm has a 2/3 thin thread-like shape, the back part is expanded in the form of an arc. The size of females is 3-5 cm, males are always shorter.
Almost the entire front part of the worm is immersed in the intestinal mucosa, as if piercing it, only the expanded tail part remains on the surface.
The whipworm feeds on tissue sap, epithelial cells and red blood cells.
The life expectancy of the helminth is 5-6 years, according to some sources up to 10 years.
How does the whipworm develop?
Human infection occurs with worm eggs through the mouth.
A larva emerges from the egg in the small intestine, penetrates the villi of the mucous membrane and remains there for up to 10 days. Then it leaves the villus into the intestinal lumen and moves to the cecum.
In the cecum, the larva attaches to the mucous membrane and develops into a worm, reaching maturity. This takes about a month.
Eggs appear in the feces of an infected person after 12 weeks. One female lays about 5,000 eggs per day.
Once in the external environment, the eggs develop at a temperature of 26-28ºC and sufficient humidity and become invasive (capable of infecting humans) after 3 weeks.
If the air temperature is below 15ºC, then the development of the eggs cannot be completed, but the embryo in the egg develops slowly. This may last 4-6 months.
The viability of a ripe egg capable of infecting a person lasts up to 2 years. Eggs are highly resistant to drying out, temperature changes, and rotting.
Trichocephalosis is distributed throughout the globe, with the exception of the Far North and desert regions.
Trichocephalosis
Trichocephalosis (ICD-10 code - B79) is a human intestinal helminthiasis caused by whipworm (Trichocephalus trichirus) and occurs primarily with damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
Whipworm infestation is one of the most common in the world. It affects 500-800 million people in the world.
According to foreign data, intense foci of trichuriasis exist in psychiatric clinics. This is due to the rapid turnover of the infection process and the low level of personal hygiene of patients.
How can you get infected?
The only source of whipworm infection is humans. The incubation period for eggs shed in feces is 17-25 days.
The most favorable conditions for development are temperature 26-30ºС, air humidity close to 100%, soil moisture 18-22%, and the presence of oxygen.
In the external environment, worm eggs remain viable for 1-2 years and can even overwinter under a thick layer of snow in a temperate climate.
Infection occurs with worm eggs through
- water (including when swimming in reservoirs),
- vegetables,
- fruits,
- berries,
- table greens,
- hands contaminated with soil.
More often infected
- children 5-14 years old,
- adults working with the land,
- workers of treatment and sewerage facilities.
Effects of whipworm on health
At a high level of infection (hundreds of individuals), inflammation of the mucous membrane of the small intestine develops when the larvae enter the human body. Upon completion of larval development, these phenomena subside.
Later, inflammation appears in the cecum during the development of young helminths due to mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, as well as due to the irritating effect of the toxic substances they secrete.
Due to injury to the intestinal wall, the possibility of penetration of bacterial microflora and the development of bacterial gastroenteritis arises.
Irritation of the nerve endings of the ileocecal region of the intestine leads to disruption of the motor and secretory functions of the stomach, duodenum, and bile ducts.
Since helminths can also absorb red blood cells (each worm absorbs up to 0.005 ml of blood per day), anemia develops with intense infections (children have 200 parasites, adults 500-800).
Symptoms of infection
The severity of symptoms depends on the number of parasites that have entered the body. The first signs of the disease appear 1-1.5 months after infection.
With a small number of worms, the symptoms are erased.
With a moderate degree of infection (200 parasites) and intensive (200-10,000 parasites), symptoms of damage to the gastrointestinal tract are observed:
- loss of appetite,
- nausea,
- vomit,
- salivation,
- flatulence,
- pain in the right ileocecal region, reminiscent of pain with appendicitis,
- intense pain in the stomach, reminiscent of pain from a peptic ulcer or gastritis,
- moderate diarrhea (diarrhea),
- headache,
- dizziness,
- irritability,
- bad dream,
- sometimes fainting and seizures.
If trichocephalosis is accompanied by bacterial infection, the course of the disease becomes significantly more severe and additional symptoms such as
- tenesmus (false urge to defecate),
- pain all over the abdomen,
- weight loss.
The development of anemia is manifested by symptoms such as:
- general weakness,
- shortness of breath on exertion,
- heartbeat,
- tachycardia,
- pale skin,
- decrease in pressure.
With a long course of the disease, signs of hypovitaminosis appear:
- dry mucous membranes,
- brittle nails,
- hair fragility.
A general decrease in immunity is accompanied by exacerbation of chronic diseases and more frequent infections.
Without treatment, the disease can last 5-7 years (up to 10 years) with a single infection. As the parasites are freed due to the end of their lifespan, the symptoms subside. The impaired functions are restored, as a rule, after a few months.
Symptoms of whipworm infection in children
Unlike adults, children are more likely to experience serious damage to the central nervous system.
Sick children
- are lagging behind in physical and mental development,
- don't sleep well
- their attention wanders
- appetite decreases.
Young children become capricious, lose weight, and often suffer from respiratory tract infections.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis consists of detecting whipworm eggs during stool examination.
X-ray and endoscopic examinations reveal inflammatory bowel phenomena.
During sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy , swelling and inflammation of the mucous membrane are detected; with intense infection, helminths that have penetrated into the mucous membrane are visible.
Treatment
Treatment of trichocephalosis is carried out in a clinic. Hospitalization is required for complications - anemia, exhaustion.
During treatment, a special diet and laxatives are not used.
Medical practice shows that the effectiveness of one course of drug treatment is 65-95%.
Three main drugs are used:
When treating young children, it is preferable to use carbendacim.
Probiotics are used to restore intestinal microflora, and enzyme preparations are used to restore gastrointestinal functions.
For anemia, iron supplements and B vitamins are needed.
The effectiveness of treatment for trichuriasis is determined on the basis of negative results of stool examination 2 times with an interval of 2 weeks.
The first study is carried out no earlier than 12-14 days after treatment.
Prevention
Compliance with the following rules is of great importance for the prevention of disease:
- using feces to fertilize the soil only after composting,
- maintaining personal hygiene rules,
- development of hygiene skills in children,
- eating only thoroughly washed fruits and vegetables,
- drinking clean or boiled water.