Colonoscopy is a medical endoscopic diagnostic method, during which the doctor examines and evaluates the condition of the inner surface of the colon using an endoscope.
Content
- 1 What diseases can be detected by this study?
- 2 What procedures can be performed during a colonoscopy?
- 3 Equipment
- 4 Is it painful to have a colonoscopy?
- 5 How is a colonoscopy performed?
- 6 How to behave after the study?
- 7 What complications may arise?
- 8 Colonoscopy indicators
- 9 What symptoms require a colonoscopy?
- 10 Contraindications
- 11 Preparing for a colonoscopy
- 12 How to examine the intestines using other methods?
What diseases can be detected by this study?
Colonoscopy is one of the most accurate methods that allows you to study the condition of the intestine from the inside, its mucous membrane, lumen, tone and other indicators. It also makes it possible to quickly and without open abdominal surgery remove benign tumors or take a biopsy of a suspicious area to find out the nature of a possible tumor.
- Cancer, tumor, colon polyp. The main goal is the early detection of cancerous tumors and their precursors, as a result of which further treatment of the pathology is simplified. Also, in the first stage of cancer, the malignant tumor is removed using colonoscopy.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane . Using colonoscopy, you can detect the inflammatory process and assess its degree, detect ulcerations, take a tissue biopsy for additional diagnostics, and also stop bleeding.
- Ulcers . Modern colonoscopes allow a detailed examination of parts of the large intestine for the purpose of early detection of even the smallest erosions and ulcers in the mucous membrane.
- Diverticula . Colonoscopy is the most informative method for diagnosing diverticulitis.
- Intestinal obstruction . With the help of colonoscopy, the true cause of some types of intestinal obstruction is revealed. Foreign bodies are also removed using a colonoscope.
What procedures can be performed during a colonoscopy?
Using colonoscopy, you can perform the following manipulations:
- remove the foreign body;
- remove polyp;
- remove the tumor;
- stop intestinal bleeding;
- restore intestinal patency during stenosis (narrowing);
- do a biopsy (take a piece of tissue for histological examination).
Equipment
In terms of its technical performance, colonoscopy is a complex method of endoscopic examination.
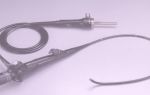
The technique is well developed, but the individual characteristics of the colon, and especially the pathological processes in it, create difficulties during the examination. Therefore, it is important that this procedure is carried out by high-level specialists using modern equipment. Colonoscopy is performed using a thin, soft and flexible fiber colonoscope or optical probe.
The flexibility of the device allows the examination to painlessly pass through all the anatomical bends of the intestine.
In many clinics, colonoscopy is performed using modern endoscopic equipment manufactured by Pentax Medical (Japan). The difference between this colonoscope is its minimal diameter and high-tech optics. (OnClinic)
The thin and flexible probe significantly reduces patient discomfort during the examination. High-quality optics allows an experienced doctor to be guaranteed to make an accurate diagnosis and identify the disease in the early stages, as well as carry out the procedure without complications.
Other equipment of the highest (expert) class from Olympus (Japan) with the ability to digitally zoom and examine in a narrow spectrum of light, allowing you to see early cancer with an area of \u200b\u200bfrom 1 mm. The equipment is processed after each patient in special washing machines (also manufactured by Olympus), which completely eliminates the possibility of transmission of infection from one patient to another. Processing in a washing machine is considered the gold standard for processing endoscopes, but leads to increased cost of the examination. However, leading clinics do not skimp on patient safety (CDC).
Videocolonoscopy
Videocolonoscopy is the most informative and accurate method for diagnosing diseases of the large intestine. It allows you to study the tone and contractility of the intestines. Its main difference from traditional colonoscopy is that the video sensor used during the examination allows the doctor to view the examined areas on the monitor screen. When studied, any area of the intestine can be significantly enlarged, which greatly simplifies the diagnosis and makes it possible to begin treatment as early as possible.
A thorough examination of the intestinal mucosa during video colonoscopy allows the doctor to notice the slightest deviations from the norm and detect pathological neoplasms ranging in size from 1 mm. If necessary, suspicious tissue can be taken for biopsy during video colonoscopy. Histological examination of the obtained tissue samples (using a magnifying microscope) will additionally help make the correct diagnosis as quickly as possible.
Expert-level equipment will allow you to identify possible pathology and begin treatment as soon as possible without the need for expensive additional studies.
After the examination, the patient receives the results of video colonoscopy in digital form.
Is it painful to have a colonoscopy?
Performing a colonoscopy on the colon is sometimes accompanied by painful sensations.
The cause of pain may be distension of the intestine with a colonoscope or air, which is introduced into the intestine to open its lumen. At this point, the patient may experience short-term pain such as painful spasms. However, many doctors, based on their experience, believe that it is better to start the procedure without prior anesthesia.
It is better to administer painkillers and antispasmodics locally during colonoscopy if there is an increased pain reaction or excessive spasm of the intestine. Drugs whose main active ingredient is lidocaine can be used as local anesthesia during colonoscopy. When applied to the desired area, it provides local anesthesia.
The advantage of pre-administered anesthesia is that the patient does not feel discomfort or pain during the colonoscopy.
When should you have a colonoscopy while you sleep?
Many studies are carried out without anesthesia: the doctor’s experience, modern equipment with adjustable endoscope rigidity and the use of local anesthetic gels for the anus make it possible to reduce discomfort to a minimum, and sometimes even avoid any pain.
Colonoscopy under anesthesia is recommended for patients who have undergone several operations or if they have experienced a painful examination.
The terms “sedation”, “general anesthesia”, “anesthesia” and “sleep colonoscopy” are the same thing. Before a procedure with anesthesia, it is necessary to undergo an examination and undergo a series of tests (for example, a blood test) to identify possible contraindications.
The patient, who is in a state of drug-induced sleep, must be under the continuous supervision of an experienced anesthesiologist during the study.
How is a colonoscopy performed?
The examination of the large intestine is carried out in a specialized room. The person undergoing the examination should undress from the waist down, including underwear, then, once prepared, will need to lie on the couch, on his left side, bending his knees and moving them towards his stomach.
The doctor carefully inserts the colonoscope through the anus, and then sequentially examines the intestinal walls.
For better visualization and a more thorough examination, the lumen of the intestinal tube is expanded and its folds are smoothed. This occurs due to a moderate supply of gas to the intestines, and the patient may experience a feeling of bloating. At the end of the study, the injected gas is removed by the doctor through a special channel of the device and the feeling of bloating disappears.
The colonoscopy procedure lasts on average from fifteen to thirty minutes.
After completing the study, the colonoscope is carefully removed from the intestine and sent to a special apparatus for disinfection.
The patient, if he has received local anesthesia or an injection of an anesthetic drug, can immediately leave the clinic after the procedure. In the case of a colonoscopy under general anesthesia, the patient after the procedure is transported to the ward, where he will remain until the anesthesia wears off.
How to behave after the study?
- If the procedure was performed without anesthesia, you can eat and drink immediately after the procedure.
- If anesthesia was performed, it is better to postpone eating for at least 45 minutes.
- If the procedure is therapeutic in nature, you may need to follow a specific diet recommended by your doctor.
- After the procedure, you should walk for 5 minutes and then sit on the toilet for 10-15 minutes in order to relax and release any remaining air. If the feeling of fullness and bloating with gases persists for longer than 30-60 minutes, you can take 8-10 tablets of finely crushed activated carbon mixed in 1/2 glass of warm boiled water, or drink 30 ml of Espumisan, also diluted in 1/2 glass of warm water .
What complications may arise?
Colonoscopy is a fairly safe examination method.
In exceptional cases, the patient may experience the following complications during or after the examination:
- perforation (perforation) of the wall of the large intestine (occurs in approximately one percent of cases);
- the patient may be bothered by slight bloating, which goes away after some time;
- bleeding may develop in the intestines (happens in approximately 0.1% of cases);
- anesthesia can lead to respiratory arrest in the patient (happens in approximately 0.5% of cases);
- after removal of polyps, symptoms such as pain in the abdominal area, as well as a slight increase in temperature (37 - 37.2 degrees) may be observed for two to three days.
The patient should urgently consult a doctor if he or she experiences the following symptoms after a colonoscopy:
- weakness;
- fatigue;
- dizziness;
- abdominal pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- diarrhea streaked with blood;
- temperature 38 degrees and above.
Colonoscopy indicators
Colonoscopy results describe the appearance of the intestinal lining.
- In healthy people, when observed through a colonoscope, it has a pale color. In this case, the color depends on the light intensity.
- Normally, the walls are covered with a thin layer of mucus and look shiny. When there is insufficient mucus, the surface of the intestines appears dull. This condition of the mucous membrane indicates the presence of pathological disorders in the large intestine.
- The surface of the intestine should be smooth and slightly striated, without ulcerations, protrusions or tubercles.
- During examination, small blood vessels of the mucous membrane and submucosa are normally clearly visible. The absence or strengthening of the vascular pattern indicates a possible pathological stretching or swelling of the submucosal membrane.
- The observed mucosal deposits are caused by the accumulation of mucus in the large intestine and normally appear as light-colored lumps.
- When should a colonoscopy be performed?
What symptoms require a colonoscopy?
Indications for the procedure are symptoms such as:
- frequent constipation,
- frequent recurring pain in the intestinal area,
- bloody or mucous discharge from the rectum;
- the presence of blood or mucus in the stool,
- unexplained weight loss, fatigue,
- feeling of intestinal fullness, tendency to frequent bloating, gas formation, flatulence,
- preparation for various gynecological operations,
- suspicion of various diseases of the large intestine,
- frequent abdominal pain,
- frequent diarrhea,
- previously identified polyps,
- anemia,
- heredity - the presence of relatives suffering from intestinal cancer,
- allergic reactions of unknown origin,
- there is an increase in the concentration of specific tumor markers in the blood test;
Contraindications
There are practically no contraindications for the procedure. The study is contraindicated only in cases of severe concomitant pathology that requires serious hospital treatment.
For example, in case of acute intestinal obstruction, acute diverticulitis or peritonitis, colonoscopy is prohibited.
Hemorrhoids are not a contraindication to colonoscopy. On the contrary, this procedure can be used to stop bleeding and examine nodes.
Preparing for a colonoscopy
Before performing a colonoscopy, special preparation is required; this is the key to high reliability of the research results.
Before undergoing a colonoscopy, the following recommendations should be followed:
- stop taking antidiarrheal and iron-containing medications;
- increase fluid intake.
Currently, preparation for a colonoscopy is carried out by ingesting special laxative solutions and following a certain diet.
Diet
Two to three days before a colonoscopy, you should follow a slag-free diet, the purpose of which is to effectively cleanse the intestines. At the same time, it is recommended to exclude from the diet foods that cause fermentation, bloating, and also increase the formation of feces.
1 day before the procedure, it is advisable to eat only liquid foods (yogurt, semolina, scrambled eggs). You can afford the most hearty lunch before 12 noon, and then only clear, low-fat chicken broth, tea and still water.
It is recommended to skip dinner the evening before the test, and not to have breakfast on the morning of the test.
Foods to Avoid
- All vegetables raw
- fruits,
- peas, beans,
- black bread,
- greenery,
- smoked products (sausage, meat, fish),
- marinade, pickles,
- pearl barley, oatmeal and millet porridge,
- chocolate, chips, nuts, seeds,
- milk, coffee,
- carbonated drinks, alcohol.
What can you eat?
- Boiled vegetables,
- fermented milk products (sour cream, cottage cheese, kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk),
- vegetable soups,
- white bread croutons, crackers, white bread,
- boiled eggs,
- lean meats (chicken, rabbit, veal, beef),
- low-fat fish (for example, hake, pike perch, carp),
- cheese, butter,
- weakly brewed tea, compotes,
- jelly, honey,
- still water, clear juices.
Purgation
Currently, special laxatives are most widely used to cleanse the intestines. It is necessary to study contraindications and choose the most suitable remedy for you. It is better to consult a doctor if possible.
As a rule, Fortrans, Endofalk, Fleet Phospho-soda, and Lavacol are used for this purpose.
The main mechanism of action of these drugs is that these drugs prevent the absorption of substances in the stomach as well as the intestines, which leads to faster movement and evacuation of contents (in the form of diarrhea) of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to the content of electrolyte salts in laxative preparations, disruption of the water-salt balance of the body is prevented.
How to take Fortrans before a colonoscopy?
The most popular is colon cleansing with Fortrans.
One sachet of the drug is designed for 20 kg of body weight. Each sachet should be diluted in one liter of warm, boiled water. If, for example, a person weighs 80 kg, then four sachets will need to be diluted in four liters of water.
Drink the resulting solution according to the scheme below.
If you are scheduled for a colonoscopy before 2 p.m.:
- Drink the entire Fortrans solution at a rate of 1 liter per hour, 1 glass every 15 minutes, from 16.00 to 20.00 the previous day.
- You can drink sweet tea in the morning if you are planning a colonoscopy WITHOUT SLEEP.
- If you are planning to have a colonoscopy DURING YOUR SLEEP, drinking any liquids, including medications, 4 hours before the test is strictly prohibited.
If you are scheduled for a colonoscopy after 2 p.m.:
- Drink half of the Fortrans solution from 18.00 to 20.00 on the day before the test.
- Drink the remaining half of Fortrans from 7.00 to 9.00 on the day of the study.
- If you are planning a colonoscopy WITHOUT SLEEP, a light meal is allowed (broths, yoghurts, jelly (without berries), tea with cookies or crackers), but not earlier than 2 hours before the colonoscopy.
- If you are planning to have a colonoscopy DURING YOUR SLEEP, drinking any liquids, including medications, 4 hours before the test is strictly prohibited.
After taking Fortrans, loose stools are possible for some time, this is normal.
How to examine the intestines using other methods?
The “golden” standard for diagnosing diseases of the colon and the most profitable examination in terms of price/quality ratio today is only colonoscopy.
Virtual colonoscopy, irrigoscopy (x-ray with barium enema), video capsule endoscopy of the colon, computed tomography - none of these studies reaches the diagnostic level of colonoscopy and are used as auxiliary studies. In addition, all of them have the main and most important drawback - during their implementation, not a single medical procedure can be performed, only an examination can be performed.