In the digestive system, this organ plays one of the most difficult
roles.
And it is she who suffers most from bad eating habits. This is due to the fact that the duodenum is the initial
section of the small intestine.
This is where the food comes from the stomach.
Content
Structure of the duodenum
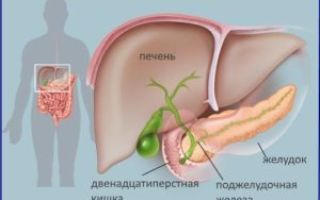
The duodenum encloses the horseshoe pancreas in the upper right abdomen.
The length of the duodenum is 20-30 cm, which is equal to approximately 12 fingers. The finger is an ancient measure of length, equal to the transverse width of the finger. Normally, the intestine has a shape similar to a U, V or S.
It is customary to distinguish 4 sections of this intestine:
- upper
- descending
- horizontal
- ascending.
The duodenum begins with an extension called
the duodenal bulb.
The size of the bulb may vary depending on the tone of the intestine and the degree of its filling.
But on average, the duodenal bulb reaches a diameter of 4 cm and a length of 3-4
cm. The duodenum ends with a transition to the jejunum,
forming a duodenal-jejunal bend.
The upper part of the intestine starts from the stomach and runs to
the right and back along the right surface of the spine.
The descending part, 9-12 cm long, from the bend of the upper intestine descends almost vertically and
ends at the lower bend of the duodenum.
The descending part of the duodenum is located in the abdominal cavity
in such a way that it comes into contact with the right kidney, renal vessels,
the initial part of the ureter, and the colon.
The head of the pancreas approaches
it from the inside In front, this part of the intestine is covered by the transverse colon and its mesentery.
The horizontal part is located below the mesentery of the transverse
colon.
The ascending part, 6-13 cm long, connects to the jejunum, forming a bend that is connected to the left leg of the diaphragm, to which it is firmly
fixed.
Innervation is provided by the vagus nerves and plexuses - the celiac, superior
mesenteric, hepatic, superior and inferior gastric and
gastroduodenal.
The entire intestinal wall is penetrated by nerve branches.
The cavity is lined with villi, which are covered with microvilli, which increases
the cell surface by 14-39 times.
Two arteries are responsible for the blood supply to the duodenum -
the superior and inferior pancreaticoduodenal.
There are cases when the mesenteric aorta compresses the duodenum
in the area of its horizontal part, which leads to its partial
obstruction.
Functions
The ducts of the two main digestive glands flow into this intestine. One is called the bile duct and comes from the liver, the other is the pancreas, from the pancreas. Under the influence of their enzymes, the digestion of proteins occurs here, which began in the stomach, carbohydrates, their digestion began in the mouth, and fats. This is the so-called cavity digestion. But cavity digestion cannot provide absorption.
Therefore, the elements formed as a result of splitting enter the brush borders of the intestine.
It is here that the final stage of the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates and fats occurs under the influence of the intestinal enzymes themselves and their absorption. In addition, calcium, magnesium and iron are absorbed in the duodenum.
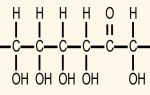
Digestion of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are organic compounds that enter the body from plant foods. They account for half of the calories a person needs per day. Thus, carbohydrates are the main source of energy obtained from nutrition.
Sources of carbohydrates are grains, legumes, vegetables, fruits, honey, sugar. They enter the body as part of starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose, fructose and glucose. In addition, plant foods contain ballast substances; they consist of cellulose and dietary fiber, which are not digested.
When carbohydrates are broken down in the duodenum, complex processes occur with the release of a large number of different enzymes. The high specificity of these enzymes allows the breakdown of all types of saccharides.
If for some reason the secretion of any enzymes is impaired, this leads to intolerance to lactose contained in milk, sucrose contained in regular sugar, and trehalose contained in mushrooms. This intolerance is characterized by the appearance of profuse diarrhea and abdominal pain after consuming foods containing these carbohydrates.
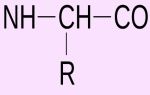
Digestion of proteins
Proteins form the basis of cells and tissues. They contain essential amino acids. Complete sources of protein, that is, containing all the essential amino acids, are animal proteins, meat, fish, dairy products, and egg whites.
The breakdown of proteins begins in the stomach. In the duodenum it continues first through the action of pancreatic enzymes, and then by the intestine’s own enzymes.
As a result of this process, a large number of peptides are released, which play an important role in ensuring the body's defense function.
Digestion of fats
In providing the body with energy, fats are in second place after carbohydrates. They contain essential unsaturated fatty acids. Essential means that the body itself is not able to synthesize them. Thus, the intake of fats into the body is necessary.
Partially, 10% of fat is processed in the stomach. In the duodenum, it is broken down first by bile acids and pancreatic enzymes, and then by the intestinal enzymes themselves.
Regardless of the quantity and quality of fat entering the body, it is completely absorbed, and no more than 5% of fat is lost in feces.
Maintaining body homeostasis
Homeostasis is the constancy of the internal environment of the body. Back in the 19th century, scientists noticed that the composition of blood and lymph remained virtually unchanged under different environmental conditions. While studying this issue, Soviet scientists found that this is provided by the gastrointestinal tract. And with a deeper study, we realized that the main function of maintaining homeostasis is performed by the duodenum.
Regardless of what food enters the body, the food mass (chyme) that comes out of the duodenum always has almost the same composition. It is closer to blood values than to the composition of food eaten.
How is this achieved? If the food is balanced and contains all the necessary components, then breakdown and absorption occurs in the duodenum, as described above. If there is an excess of one component and a deficiency of others in food, then the body takes the missing elements from its reserves, most often from the blood.
If such a imbalance in the incoming food persists for a long time, this may adversely affect the composition of the blood. This process is poorly affected by fasting, mono-diets, and separate meals.
It has been proven that as long as the mechanisms for maintaining homeostasis in the body are not disrupted, environmental influences cannot have a damaging effect on it.
Diseases of the duodenum
As noted above, the food bolus from the stomach enters the duodenum. This makes it vulnerable to increased acidity of gastric juice. As a result, the duodenum is susceptible to peptic ulcers .
Inflammation of the wall of the duodenum, most often only the mucous membrane, is possible. This disease is called duodenitis .
An isolated lesion of the mucous membrane of the duodenal bulb is called bulbitis, and the area of the large duodenal papilla is called sphincteritis.
According to the Central Research Institute of Gastroenterology, the incidence of intestinal diverticulum has increased over the past decades in economically developed countries. This is associated with insufficient consumption of coarse fiber.
A duodenal diverticulum is a congenital or acquired protrusion of the wall of a hollow organ. Most often it is localized in the duodenum.
Irritable bowel syndrome is a disease that affects both the small and large intestines.
Infectious and viral diseases - can affect the intestines either through infection from other people or through poor-quality food, which leads to poisoning.
Helminthiasis, infection with bovine or pork tapeworm.
Prevention measures
Paying attention to your diet will help protect the duodenum from damage.
- You should not eat food that is too hot or too cold.
- Chew food thoroughly so that the pulp enters the duodenum, because the stomach and intestines do not have teeth.
- You should not wash down food with cold drinks, as this opens the sphincter, and all food enters the duodenum undigested by gastric juice.
- Eat food in a good mood and without rushing.
- Monitor normal stomach acidity.
- Follow the rules of hygiene - wash your hands and food.


 (6 ratings, average: 4,67 out of 5)
(6 ratings, average: 4,67 out of 5)